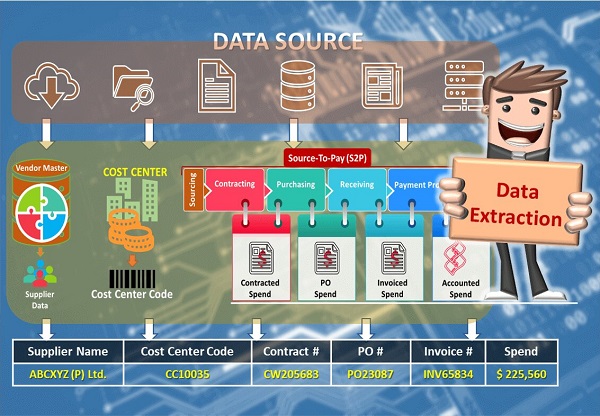
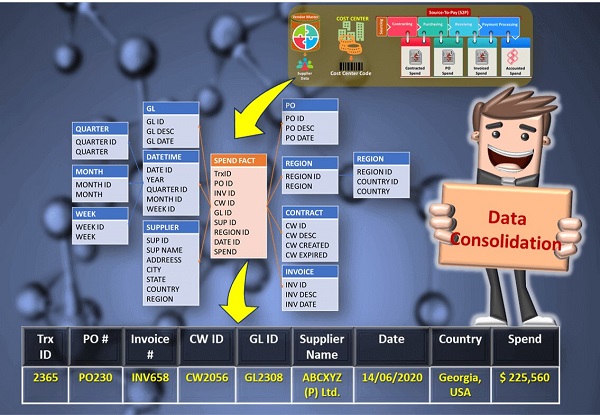
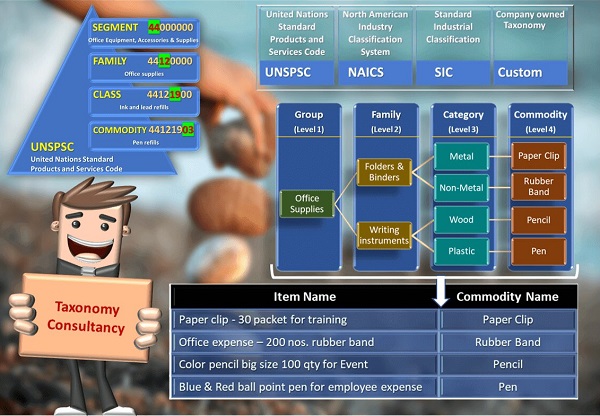
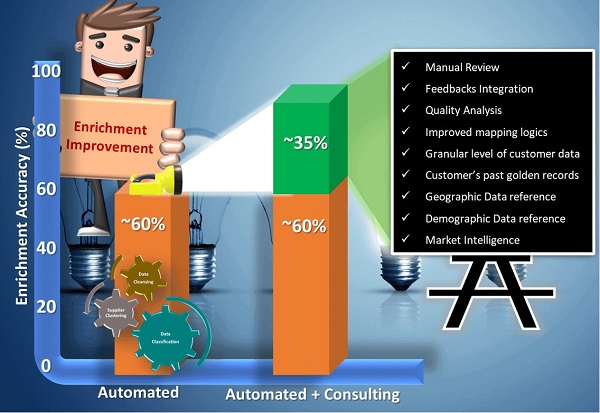
Data Extraction
Data analysis starts with a company's raw transactional and operational data. Data Sources are single or many data storage locations like Cloud, ERP, Datawarehouse, flat files, etc. Collecting and extracting data is the initial stage in an ETL process (extract, transform, and load). The goal of ETL is to prepare data for analysis or business intelligence (BI). There are 2 types of data extraction methods:
- Logical Extraction:. It is the first step in creating a physical data extraction plan.
- Full Extraction : Data copied from the source system in its entirety, even if untimestamped.
- Incremental Extraction : This method extracts data in increments. Timestamps can monitor new or changed data.
- Physical Extraction Extract data from the source system logically or physically.
- Online Extraction : The staging area processes data directly from the source system.
- Offline Extraction : In lieu of directly extracting data from the source, it is obtained from an external location (flat files, or some dump files in a specified format).
Data analysis starts with a company's raw transactional and operational data. Data Sources are single or many data storage locations like Cloud, ERP, Datawarehouse, flat files, etc. Collecting and extracting data is the initial stage in an ETL process (extract, transform, and load). The goal of ETL is to prepare data for analysis or business intelligence (BI). There are 2 types of data extraction methods:
- Logical Extraction:. It is the first step in creating a physical data extraction plan.
- Full Extraction : Data copied from the source system in its entirety, even if untimestamped.
- Incremental Extraction : This method extracts data in increments. Timestamps can monitor new or changed data.
- Physical Extraction Extract data from the source system logically or physically.
- Online Extraction : The staging area processes data directly from the source system.
- Offline Extraction : In lieu of directly extracting data from the source, it is obtained from an external location (flat files, or some dump files in a specified format).
In a data warehouse, designing and developing an extraction process is a critical and time-consuming operation. A logical integration flow or physical process is created, and private data is secured. Because data extraction is the first stage in data analysis, it involves business executives, competent data specialists, and a good data extraction ETL tool or automated programming script.